Introduction
PLC stands for Programmable Logic Control is simply a special computer that is programmed to control certain processes in industries.
PLCs are used for several key reasons, such as improving the efficiency and reliability of industrial processes, reducing the cost and complexity of wiring, and enabling easy modification of the control logic. The PLC performs the logic functions of relays, timers and counters.
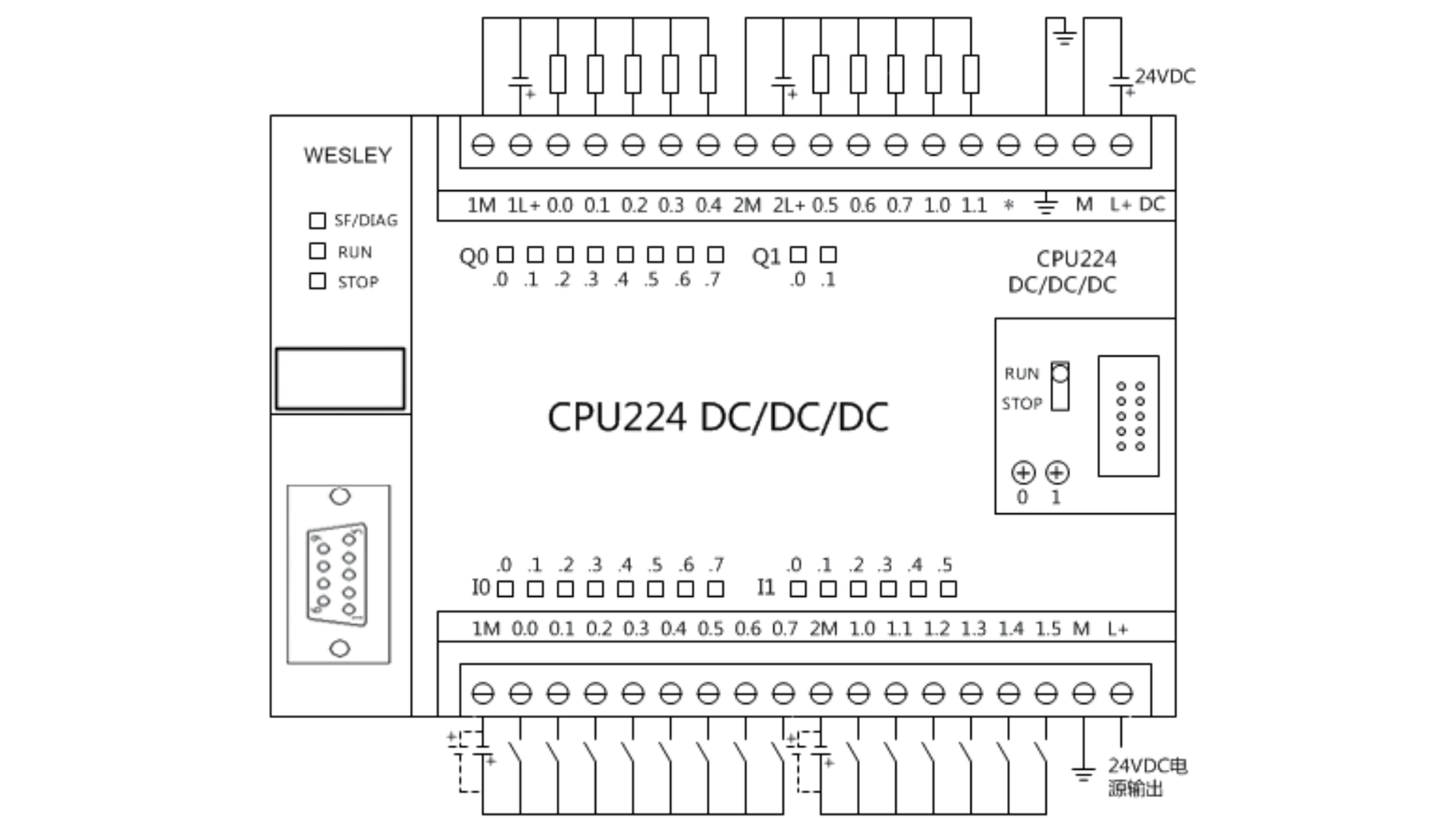
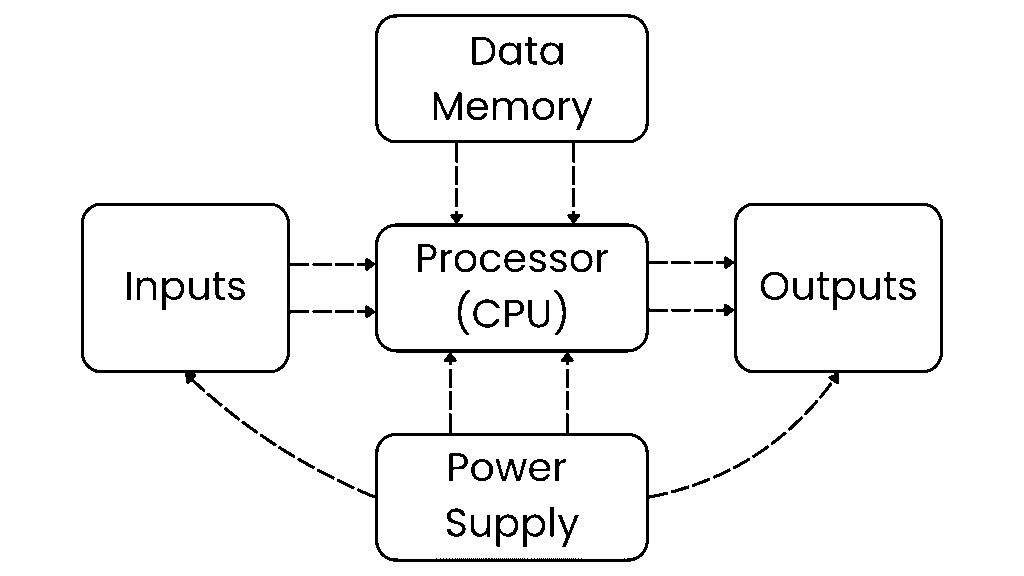
What is the main component of PLC
- Central Processor Unit (CPU): This unit containing the microprocessor and this interprets the input signals and carries out the control actions, according to the program stored in its memory, communicating the decisions as action signals to the outputs.
- Memory: The memory unit is where the program is stored that is to be used for the control actions to be exercised by the microprocessor and data stored from the input for processing and for the output for outputting.
- Power Supply: The power supply unit is needed to convert the mains a.c. voltage to the low d.c. voltage (5 V) necessary for the processor and the circuits in the input and output interface modules.
- Inputs: These modules connect the PLC to input devices such as sensors, switches, and push buttons. They convert the signals from these devices into a logic level that the CPU can understand.
- Outputs: These modules connect the PLC to output devices like motors, solenoids, lights, and alarms. They convert the control signals from the CPU into a voltage or current that can operate these devices.
What are the most popular PLC programming languages
There are 5 languages that are all a part of the IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission):
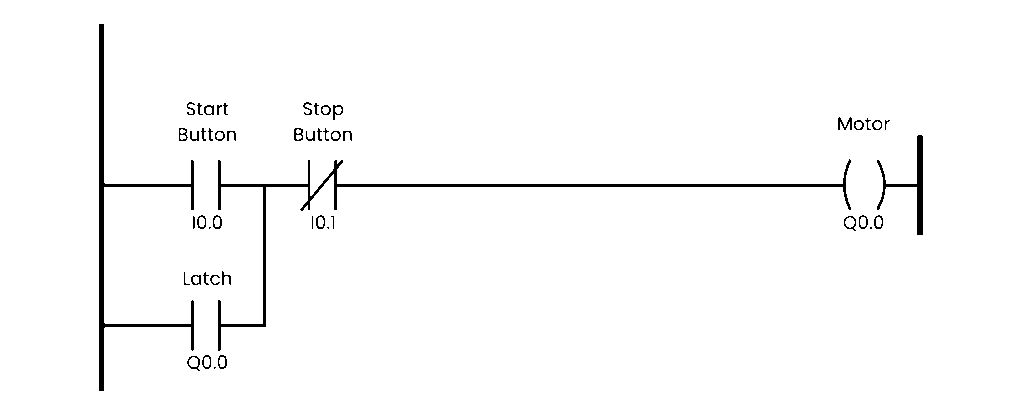
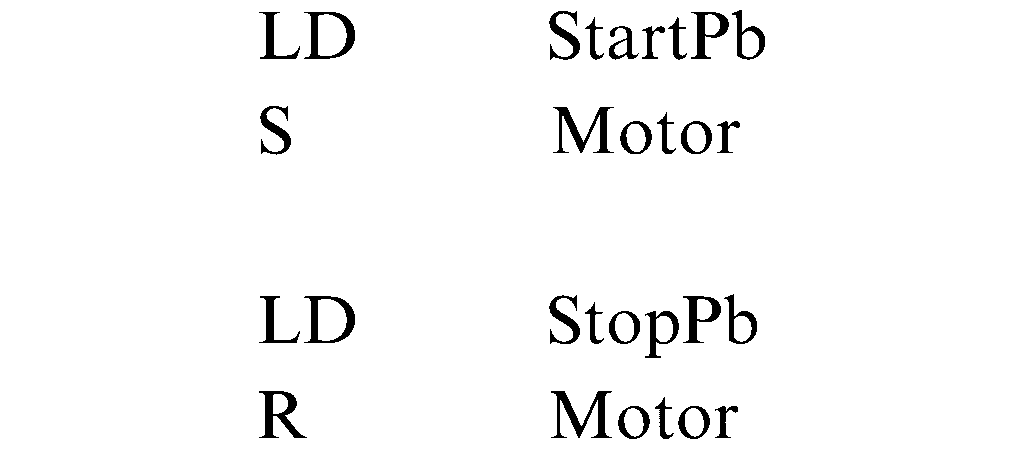
1- Ladder Diagram (LD): Ladder Diagram is the most popular PLC programming language. Many programmers prefer to start with (LD) Because it is easy to learn and understand and easy to maintenance and troubleshooting, also most companies want to hire engineers who can program with ladder diagram.
Ladder logic is by far the most popular programming language in use because of its resemblance to hard-wire control diagrams.so it is unsuitable for complex programs.
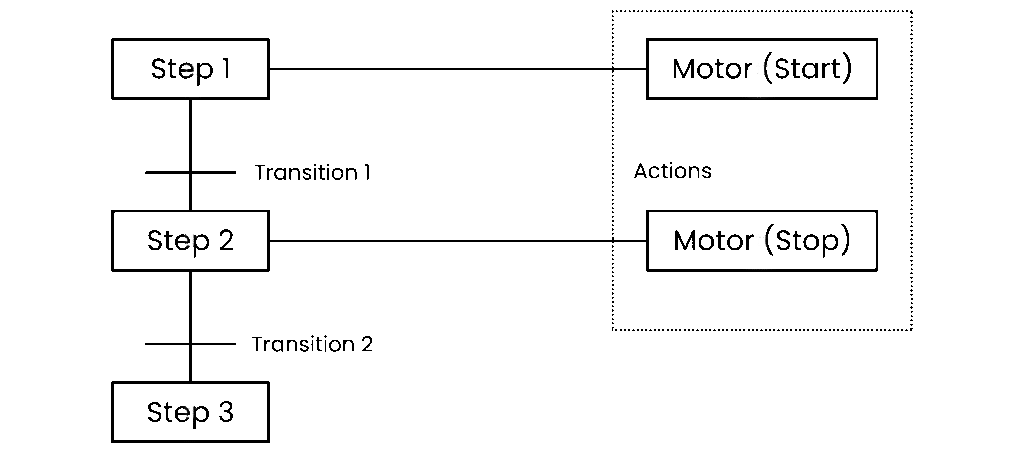
2- Sequential Function Charts (SFC): These are similar to flowcharts, but much more powerful. SFC programming offers a graphical method of organizing the program. The three main components of an SFC are steps, actions and transitions.
3- Instruction List (IL): This low-level language is similar to Assembly language and is useful in cases where small functions are repeated often. Although it is powerful, it is considered to be difficult to learn.
4- Structured Text (ST): is a high-level textual language. It is very flexible and intuitive for writing control algorithms. is a high-level textual language that is a Pascal like language. It is very flexible and intuitive for writing control algorithms. People trained in computer programming languages often find it the easiest language to use for programming control logic.
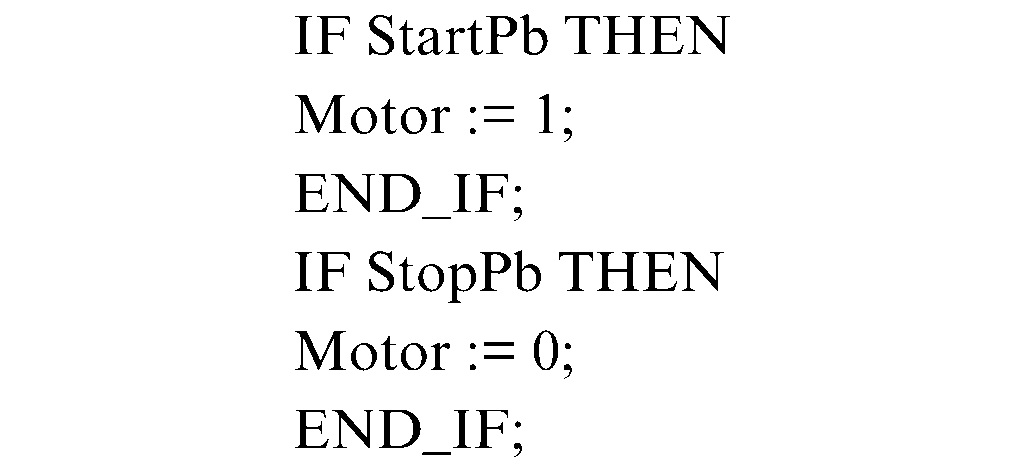
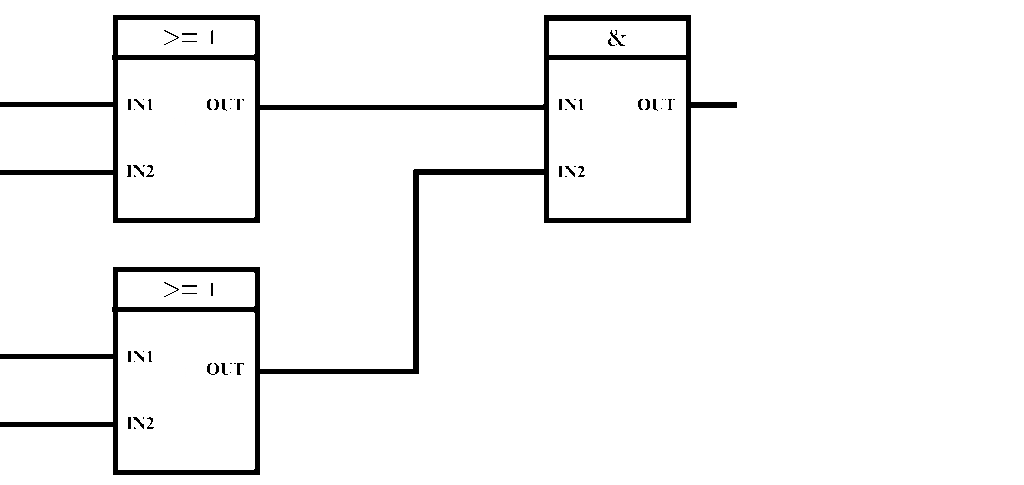
5- Function Block Diagram (FBD): FBD is a graphical language. In FBD, program elements appear as blocks which are “wired” together in a manner resembling a circuit diagram. FBD is most useful in those applications involving a high degree of information/data flow between control components, such as process control.
Advantages
- The control software is stored locally, so in the event of a building energy management system failure, the PLC can carry on.
- The connections between the PLC inputs and outputs are made by the software and not lots of separate physical wires.
- PLCs are smaller than hard wired relay banks, but can still use relays where needed.
- PLCs are easy to reprogram.
- Fault finding is easier and faster with PLCs.
- You can load the same programmed onto multiple PLC units to save time.
- You can expand the inputs and outputs with more cards.